What is Waste-to-Energy?
Ecologically Sound, Cost-Effective Energy
Waste-to-energy (WtE), also known as energy-from waste (EfW), is a vital part of a strong and sustainable waste management chain. Fully complementary to recycling, it is an economically and ecologically sound way to provide a renewable source for energy while diverting waste from landfills.
For every ton of municipal solid waste processed at waste-to-energy (WtE) facilities, greenhouse gas emissions are reduced by approximately one ton. WtE plants provide a safe waste disposal option that complements (not replaces) recycling. Recycling rates have actually increased in municipalities that have WtE plants. WtE technology supports business and industry "zero-waste-to-landfill" initiatives.
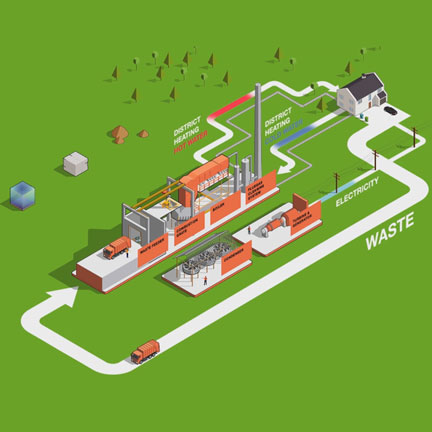
A WtE plant converts solid waste into electricity and/or heat - an ecological, cost-effective way of energy recovery.
A waste-to-energy plant converts municipal and industrial solid waste into electricity and/or heat for industrial processing and for district heating systems – an ecologically sound, cost-effective means of energy recovery. The energy plant works by burning waste at high temperatures and using the heat to make steam. The steam then drives a turbine that creates electricity and/or provides district heating and cooling.
Recover valuable resources
Harnessing energy from waste isn’t just a trash disposal method. It’s a way to recover valuable resources. Today, it is possible to reuse 90% of the metals contained in the bottom ash. And the remaining clinker can be reused as road material.
The results and benefits are proven:
- Avoids methane emissions from landfills
- Offsets greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from fossil fuel electrical production
- Recovers/recycles valuable resources, such as metals
- Produces clean, reliable base-loaded energy and steam
- Uses less land per megawatt than other renewable energy sources
- Sustainable and steady renewable fuel source (compared to wind and solar)
- Destroys chemical waste / conventional HAPs
- Results in low emission levels, typically well below permitted levels
- Catalytically destroys NOx, dioxins and furans using an SCR
High efficiency and low emissions
Waste to energy is one of the most robust and effective alternative energy options to reduce CO2 emissions and replace fossil fuels. Approximately 2/3 of household waste is categorized as biomass. Therefore, we can recover 2/3 as CO2-neutral energy and reduce our dependence on fossil fuels.
In Europe, 50 million tons of waste is converted into valuable energy through EfW technology, supplying 27 million Europeans with electricity. Still, 50% of municipal solid waste becomes landfill. This releases greenhouse gasses like methane. Our energy from waste technology eliminates these emissions.
Our goals are two-fold: to maximize production and efficiency to meet energy needs, and to reduce our environmental footprint.
Waste facts
- 4 tons of waste equals 1 ton of oil
- 2 tons of waste equals 1 ton of coal
B&W is Part of ISWA EfW Technologies Publication
As a member of the International Solid Waste Association (ISWA), B&W is proud to be part of ISWA’s White Book on Energy-from-Waste Technologies, a publication which provides a comprehensive overview of the technical, economic, legislative, institutional, social, and environmental aspects of the available thermal technologies which produce energy from waste (EfW). We were part of the working group that produced this publication and directly contributed to its development.

A Circular Economy
Waste to energy is one of the most robust and effective alternative energy options to reduce methane and CO2 emissions.
As urbanization and spending on consumables increases, more solid waste is generated. The amount of solid waste has grown over the last century to more than 3 million tons now generated per day globally, and the number is expected to double by 2025 (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development).
Solid waste management is often one of the greatest costs to municipal budgets. Increasing the amount of municipal solid waste in landfills translates to increases in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, air and odor pollution, and soil and water contamination.
Sustainable waste management
To reduce the size, cost and environmental impacts of landfills, many regions are shifting from a linear economy (make-use-dispose) to a more circular economy model, where materials are made, used and reused to their fullest extent. Complementary to recycling, WtE plants extend the useful life of the solid waste, converting it into electricity and/or heat for industrial processing and district heating systems, filtering out harmful substances and recovering metals and other material for reuse. WtE is one of the most robust and effective energy options to produce power while treating waste and reducing emissions as an alternative to fossil fuels.