Bubbling Fluidized-Bed (BFB) Boilers
 With an experience base of more than 200 BFB units worldwide, B&W’s BFB boilers are helping the world realize the promise of clean energy from a wide variety of fuels.
With an experience base of more than 200 BFB units worldwide, B&W’s BFB boilers are helping the world realize the promise of clean energy from a wide variety of fuels.
Our BFB boilers are designed to allow a wide range of fuels to be burned, separately or in combination. The ability to utilize various fuel sources and types provides owners with the flexibility to take advantage of opportunity fuels and control fuel costs. This is necessary because fuel properties vary widely. For example, biomass fuels have a wide range of moisture and heating values depending upon their source and the time of year.
BFB boilers can also be an integral component of the world’s decarbonization efforts. By combining traditional bioenergy production, such as B&W’s bubbling fluidized-bed boilers, with carbon capture and sequestration technologies, energy can be produced with a net-negative carbon intensity (CI) output. Read more about our BECCS capabilities.
B&W’s advantage
B&W’s bubbling fluidized-bed boiler is designed with reliability in mind. Several features combine to provide low maintenance costs, high availability and long-term reliability:
- An open bottom design permits easy removal of oversized or foreign material.
- A water-cooled, gas-tight lower furnace eliminates the potential for gas leaks caused from refractory damage.
- Bottom-supported hoppers remove load from the boiler, reduce capital requirements, and reduce potential mechanical stresses between water-cooled and non-cooled components.
- Rapidly responds to changes in fuel and steam demands.
Incorporated in our design are these features to reduce maintenance costs:
- No wear parts
- No moving parts
- No water-cooled screws or beams
- No cinder re-injection system
- Long-lasting bubble caps

Open bottom furnace – results in complete debris removal with lower capital costs and maintenance expenses.
Underbed ash removal system – consists of bottom-supported hoppers which isolate the bubbling bed foundation and steel from the boiler steel. This design is considered an advantage and facilitates retrofitting an existing top-supported unit to a BFB.
Bubble cap and air distribution system design – allows removal of large tramp material while durable construction rarely requires replacement.
Viable fuels for a BFB boiler

- Biomass
- Wood waste
- Bark chips
- Straw
- Sugar cane waste
- Agricultural waste
- Paper mill and recycled paper facility sludge
- Sewage sludge
- Tire-derived fuels (in combination)
- Oil
- Natural gas
- Coal (in combination)
- Peat
Environmental benefits with BFB technology
Nitrogen oxides (NOX) - Due to the low temperature combustion processes that occur in the bubbling bed, NOX generation is inherently lower than that of a stoker-fired boiler. A selective catalytic reduction (SCR) system can be located before dust removal equipment to further reduce NOX.
Carbon monoxide (CO) and volatile organic compounds (VOC) - Due to the intimate contact between the bed material and fuel, improved fuel burnout occurs. This results in very low CO and VOC emissions.
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) - The intimate contact between the fuel and bed material allows for in-bed capture of SO2. When burning biomass in combination with sulfur fuels, alkali normally present in the biomass will result in reduced SO2. Limestone can also be added to the bed material for greater SO2 capture.
Particulate - Improved carbon burnout compared with a stoker boiler reduces the potential for fires in back-end environmental equipment. This allows for the use of a baghouse to meet lower particulate requirements.
Specifications
Design features:
- Top- or bottom-supported
- One- or two-drum designs
- New or retrofit boiler applications
- Provides an option to reduce SO2 and NOX emissions
- Superior to other technologies for burning wet wood-based fuels – between approximately 2800 and 3500 Btu/lb HHV (6513 and 8141 kJ/kg) without support fuels
Capacity:
- Bottom-supported: Up to 225,000 lb/h (28.4 kg/s)
- Top-supported: From 225,000 to 1,000,000 lb/h (28.4 to 126 kg/s)
- Steam pressure: To 2600 psig (17.9 MPa)
- Steam temperature: To 1000F (538C)
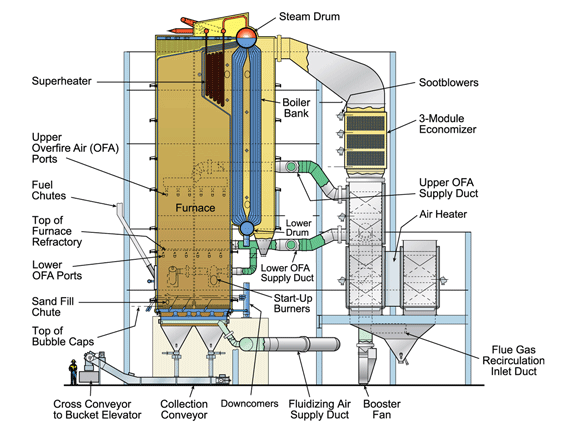
B&W Bottom-Supported BFB Boiler

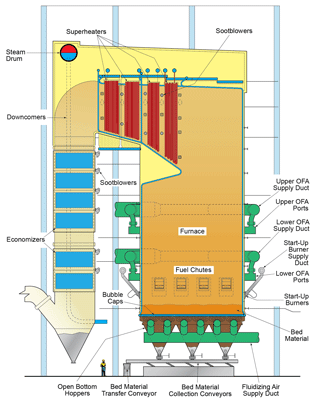
B&W Top-Supported BFB Boiler
